Visual-Sonar SLAM: Monocular ORB-SLAM2 + Sonar in HoloOcean simulation
Correcting Scale Ambiguity of Monocular SLAM with Absolute Sonar Range Measurements, utilizing captured data from HoloOcean simulation (Unreal Engine).
Goals
In this post, I want to walk you through some curiosities:
- understand scale ambiguity problem in monocular SLAM
- understand multi-beam sonar basics
- absolute sonar measurements can correct scale of monocular SLAM, but needs to obtain camera-sonar correspondences -> understand how to obtain these correspondences
- understand how to obtain camera, sonar data from HoloOcean simulation
- implement ORB-SLAM2 + ros2 package: scale estimation/correction of monocular ORB-SLAM2 from HoloOcean data
Monocular SLAM and Scale Ambiguity problem
Monocular SLAM
For a robot to navigate in an unknown environment, it basically needs to answer two questions: “What is around me?” and “Where am I?” (relative to surroundings, and past positions). SLAM (simultaneuous localization and mapping) helps robot to answer those questions, utilizing sensors data.
If a single camera is the only sensor that SLAM uses, then it is called Monocular SLAM. So how do Localization and Mapping task work using only a sequence of camera images?
 Monocular Localization and Mapping
Monocular Localization and Mapping
For every two adjacent frames, Localization does three main steps: 1) features extraction (each frame), 2) features matching (between 2 frames), 3) estimate essential matrix (representing relative camera motion). For the Mapping task, it utilized those matched features, then triangulate those 2D points to obtain 3D points. As more frames are processed, a cumulation of 3D points represent the mapped objects or environment.
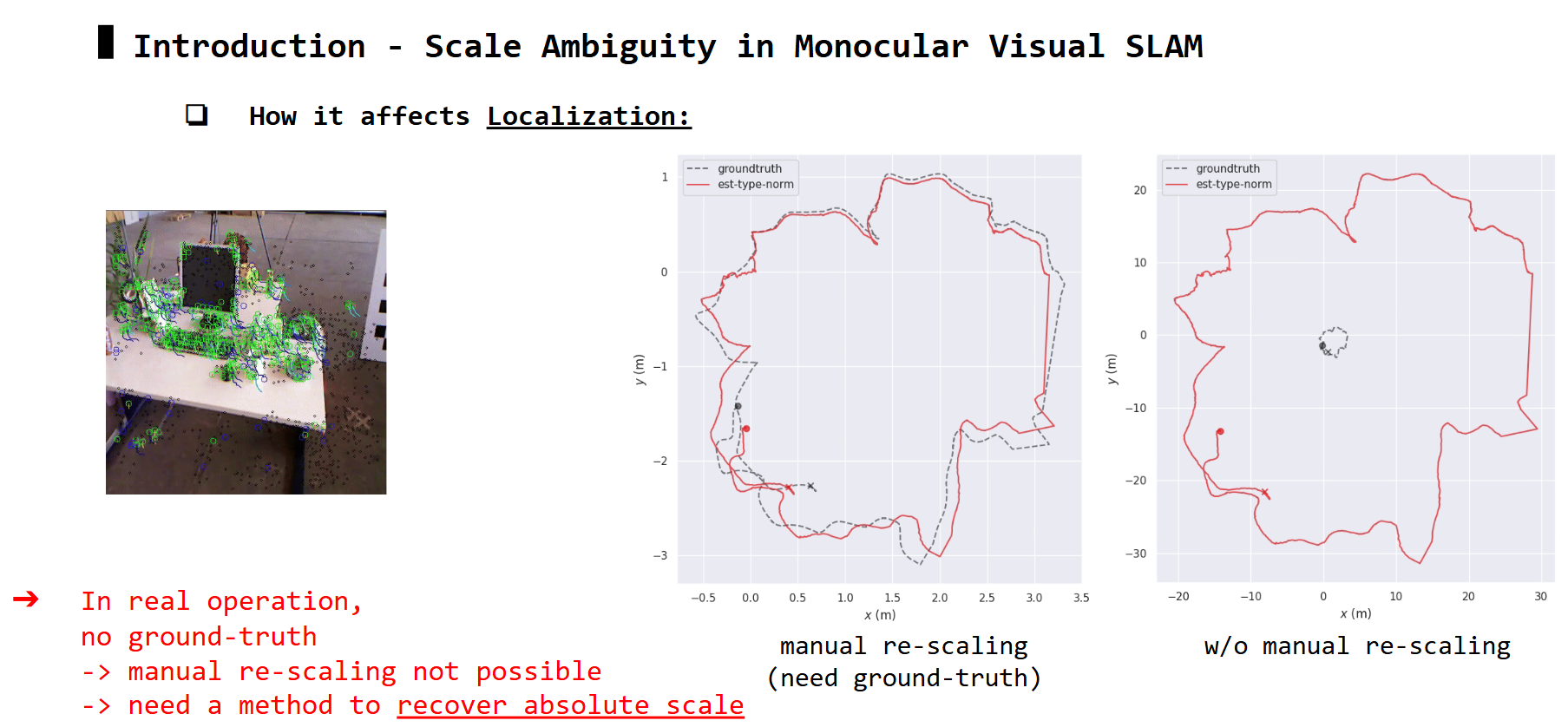
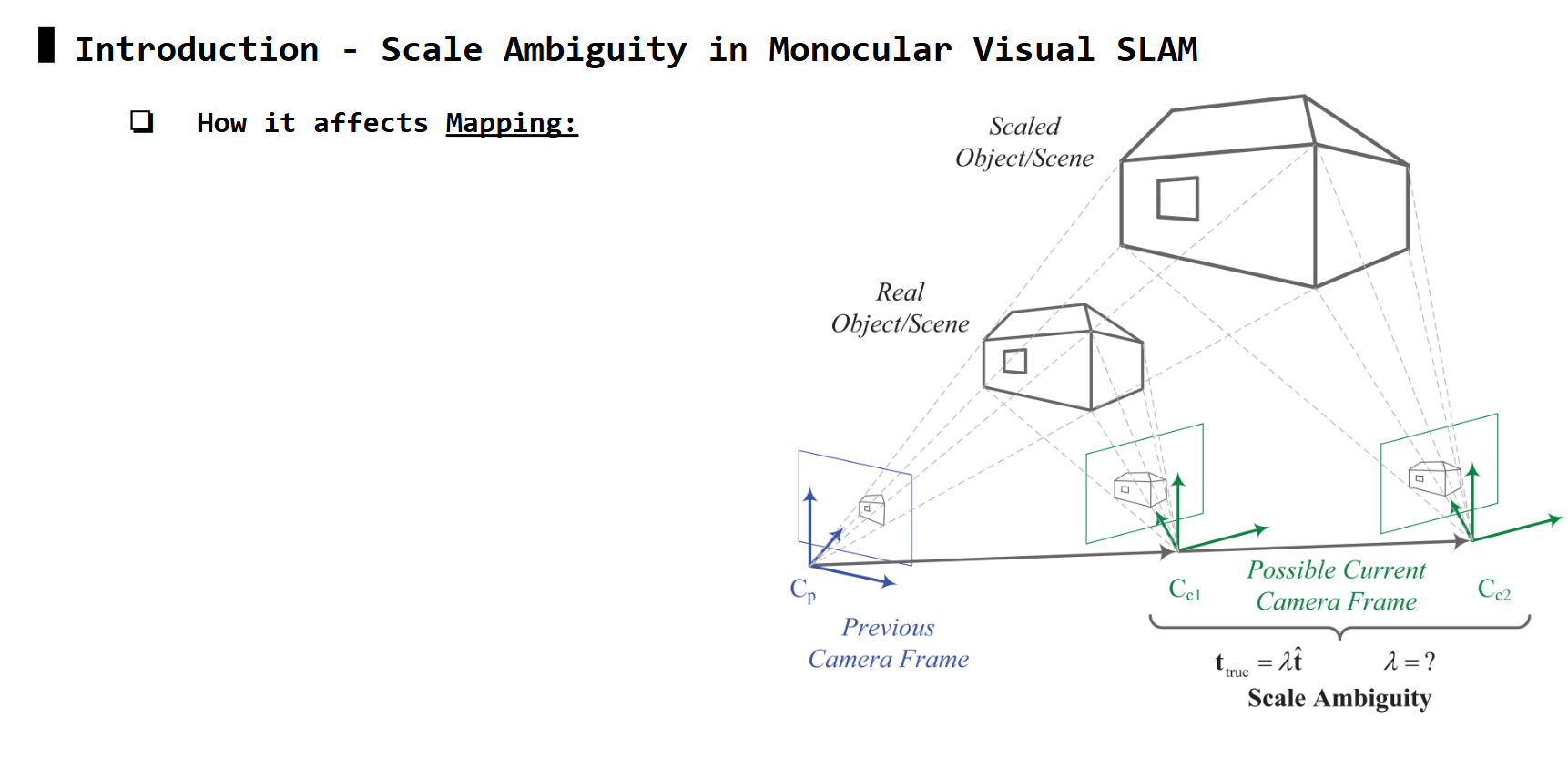
Scale Ambiguity problem
For every matched pair of features P1 & P2, the third step estimating essential matrix (E) uses the epipolar constraint equation to solve for its values.
However, P1 and P2 are normalized coordinates in image plane, thus they no long have the true depth information z. Therefore, the solution to this equation has two types of ambiguities: ambiguity along epipolar line, and ambiguity along baseline.
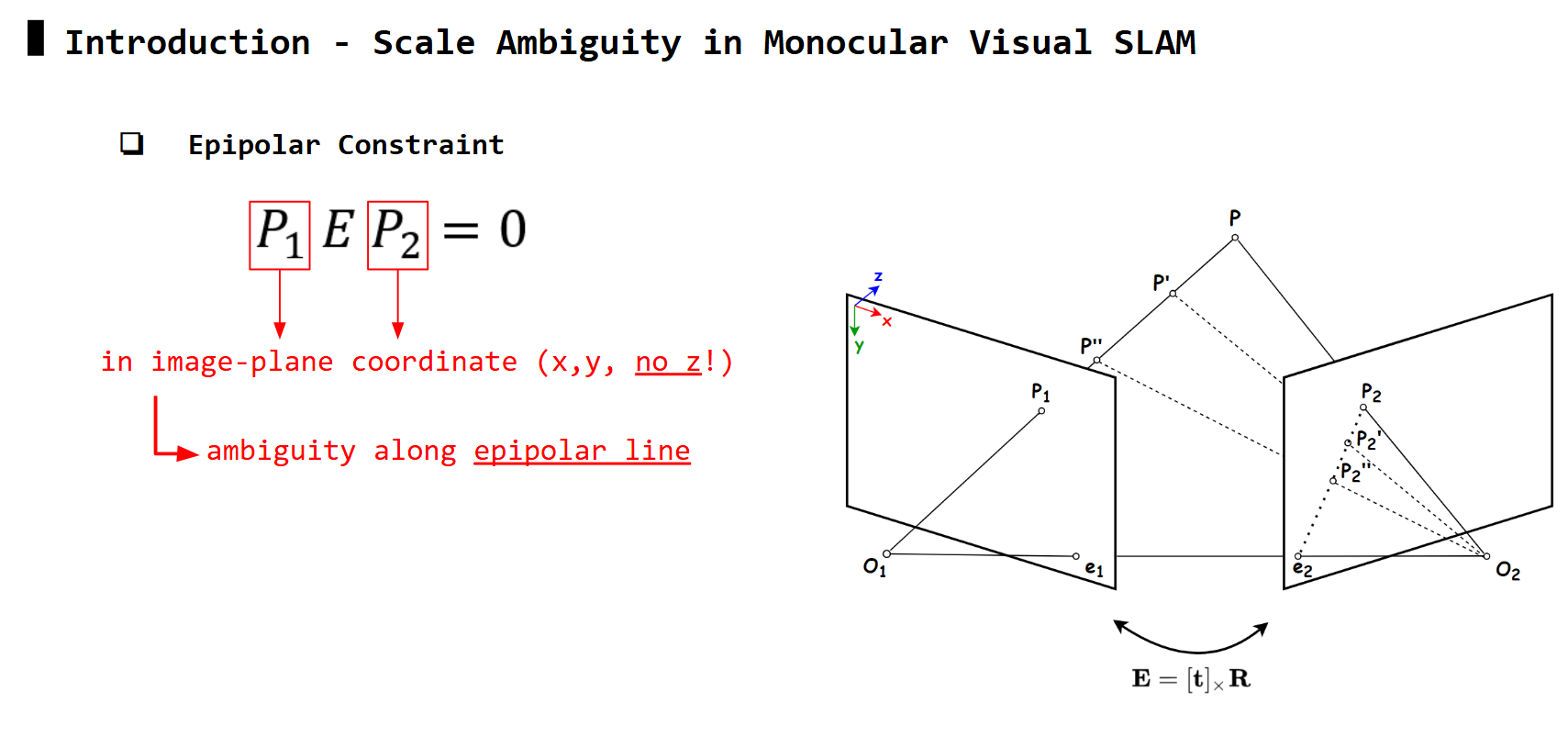 Ambiguity along epipolar line: any points
Ambiguity along epipolar line: any points P2', P2'', .. along epipolar line also satisfy equation similar to P2
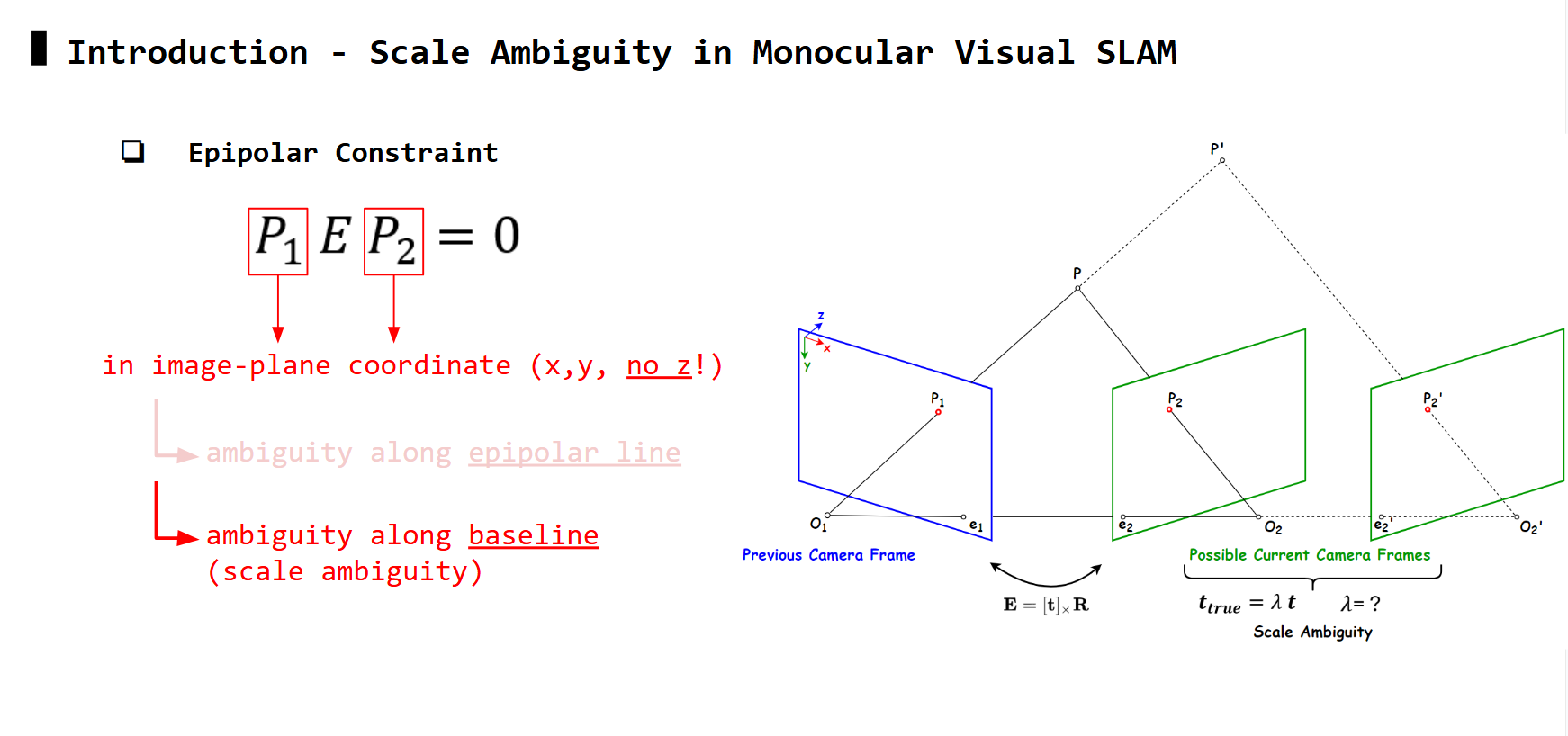 Ambiguity along baseline: frames along the baseline also satisfy equation
Ambiguity along baseline: frames along the baseline also satisfy equation
Matching features P1 and P2 may avoid ambiguity along epipolar line, but it still suffer from ambiguity along baseline. In this case, the solution of E in the epipolar equation can only be up to a scale, for the translation part (i.e: \(t_{true} = \lambda t_{est}\), can solve for \(t_{est}\) but not \(\lambda\) ). This is also known as scale ambiguity.
How this affects Localization and Mapping
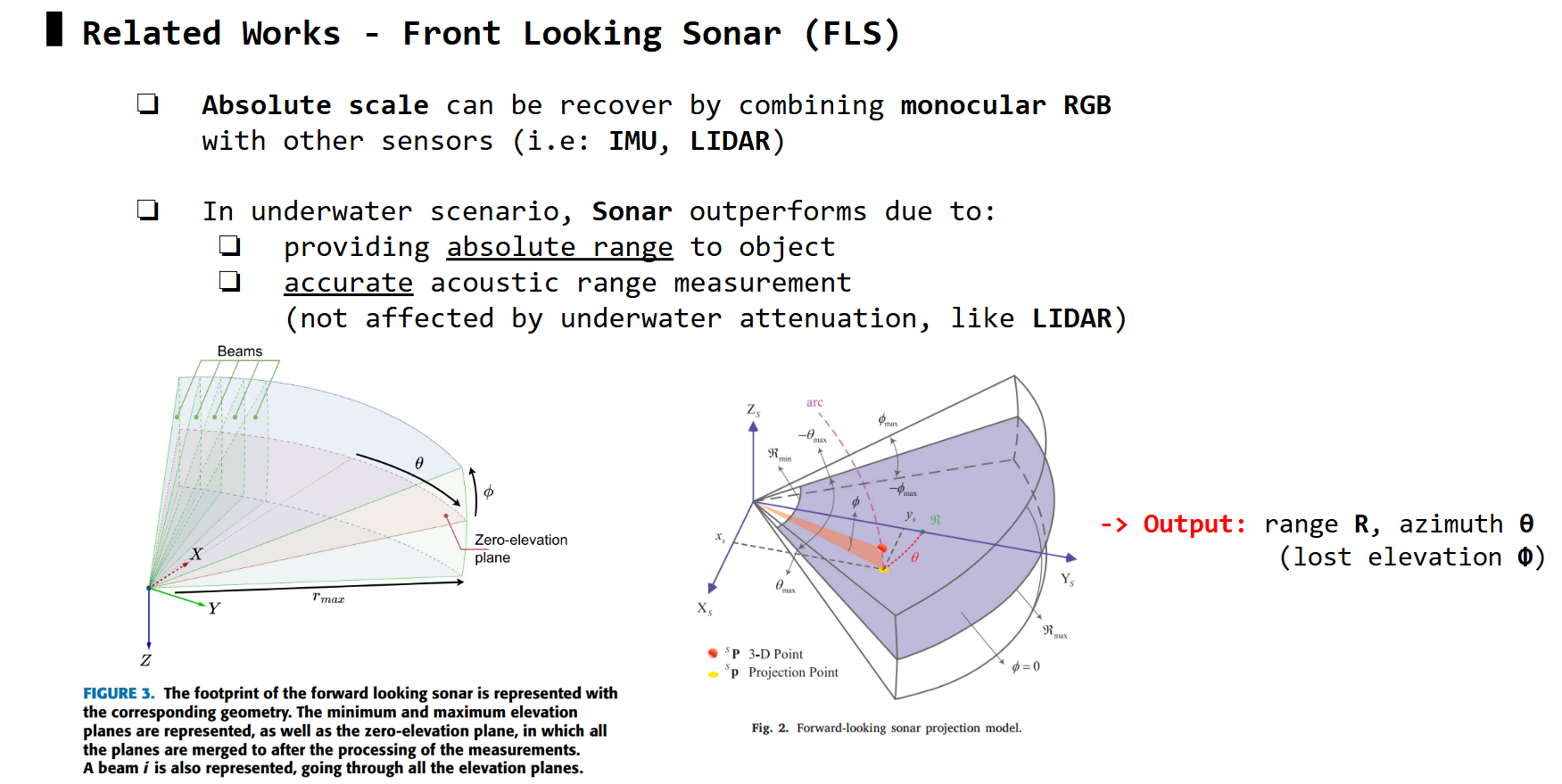
Multi-beam Sonar
Basically, for a target 3D point in underwater, multi-beam sonar outputs range R (absolute distance from sonar sensor to target), azimuth \(\theta\) (angle between center-beam axis and the target beam). However, the elevation \phi (vertical position of the 3D target relative to 0-elevation plane of sonar) is lost
How Sonar range measurements can correct scale of Monocular SLAM
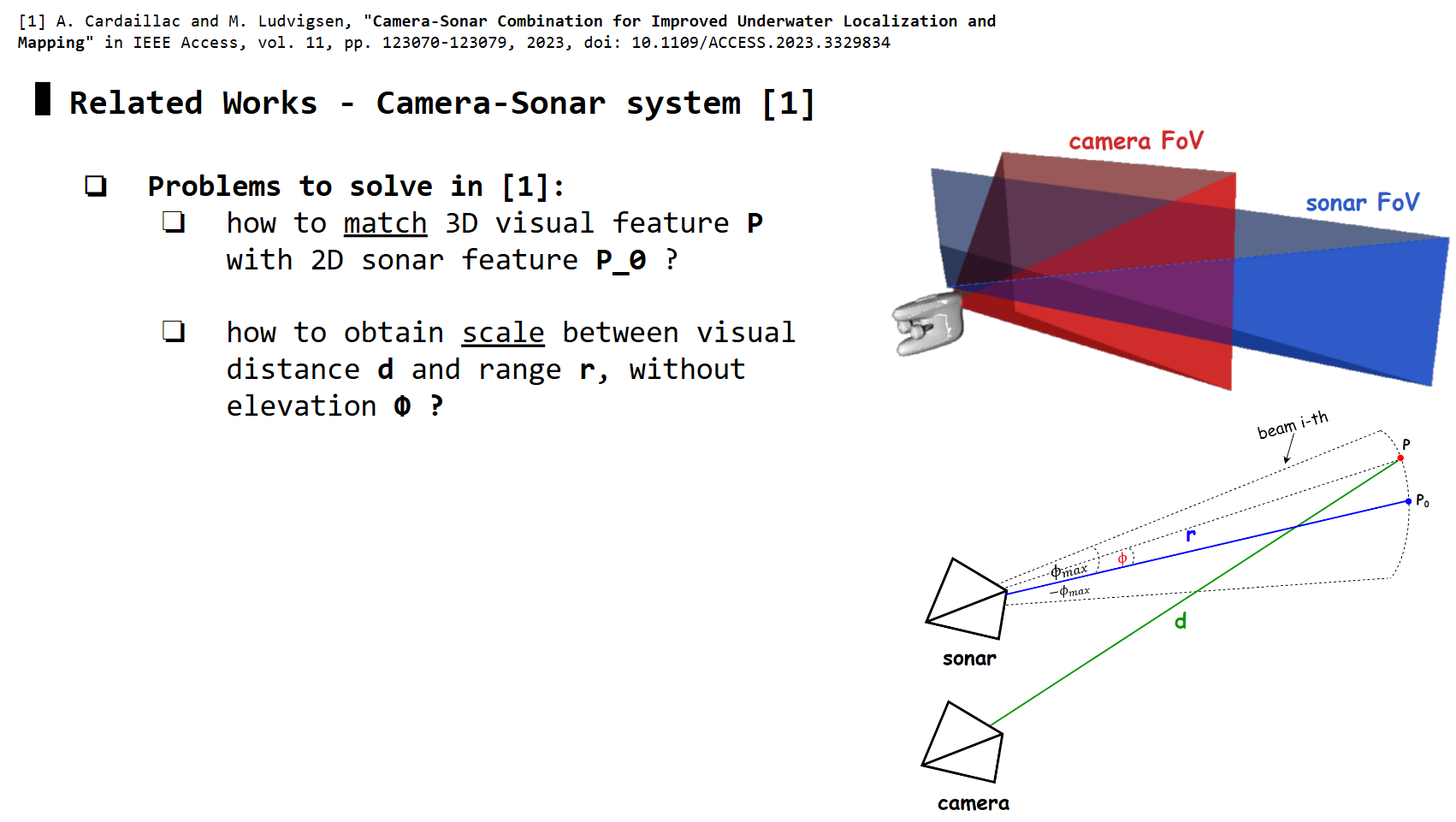 Camera and Sonar with overlapped FoV, and observing the same 3D point
Camera and Sonar with overlapped FoV, and observing the same 3D point P
Monocular SLAM frameworks (i.e: ORB-SLAM2) can estimate visual distance d from camera to P, whereas sonar captures the absolute distance r from sonar to P. How do we use r to correct d?
-> We need to match camera features with sonar features first (camera-sonar correspondences), making sure they are observing the same P, then use their relative geometry to estimate the scale \(d_{true} / d_{est}\)
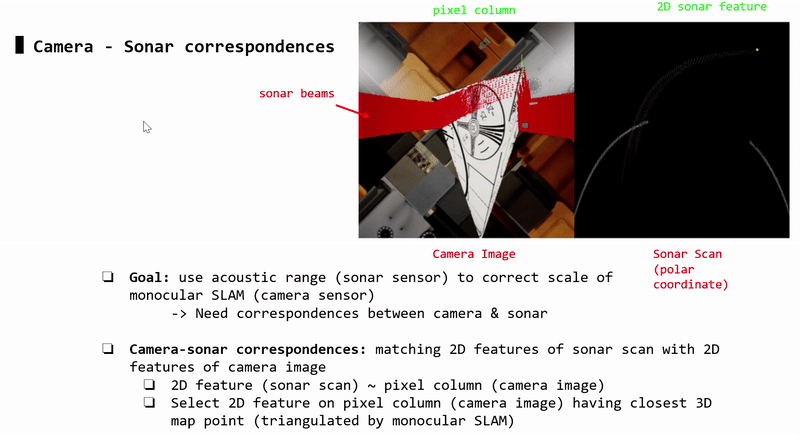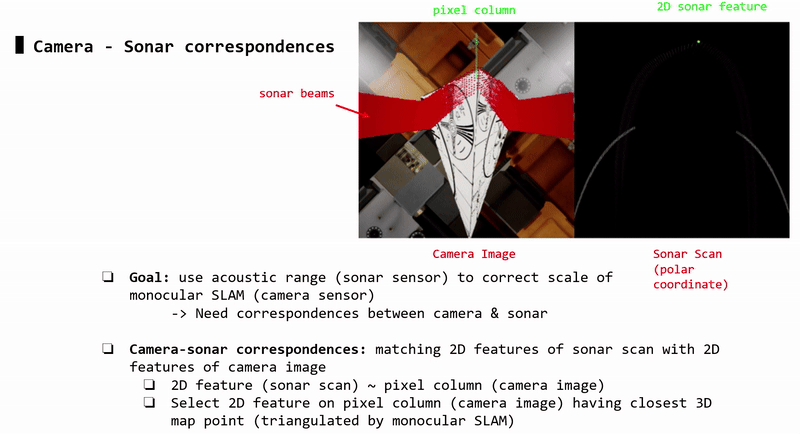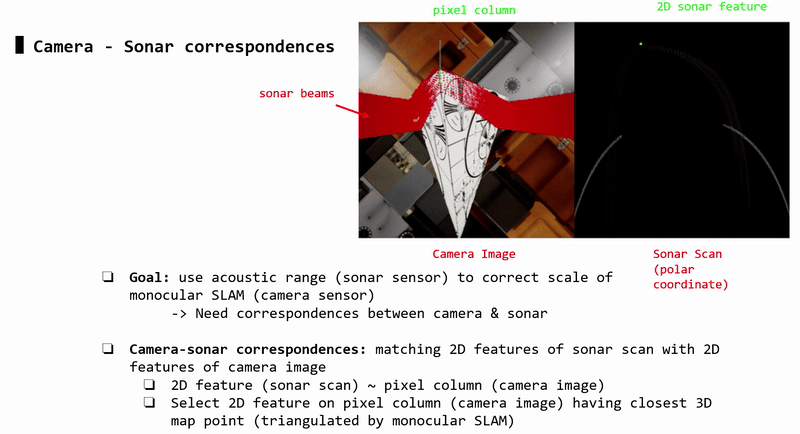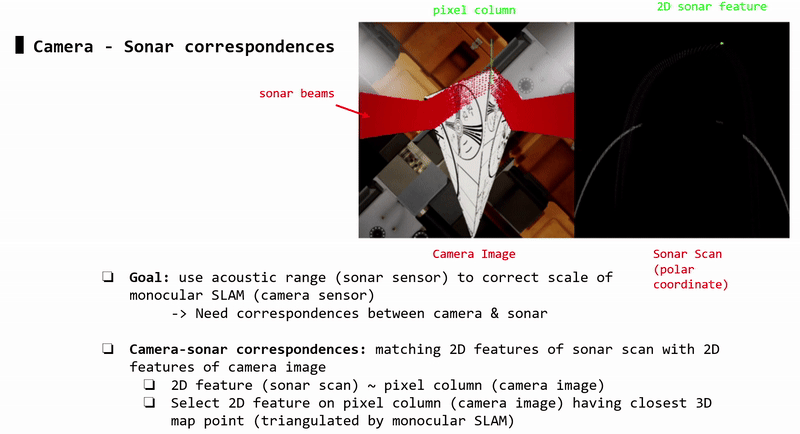
Camera-Sonar Correspondences
Each sonar 2D feature (sonar image) corresponds to a pixel column (camera image). Each pixel column may contain 2D features (i.e: detected by ORB-SLAM2). Each 2D feature corresponds to a 3D triangulated point.
-> Each sonar 2D feature (sonar image) is matched with the 2D pixel feature (camera image) that has closest 3D triangulated point (compared to other 2D pixel features in that pixel column)
Scale Estimation / Correction
For not too close stand off distances between AUV and target object, the scale \(d_{true} / d_{est}\) can be approximately estimated by \(r / d_{est}\)
Implementation: Monocular ORB-SLAM2 + ROS2
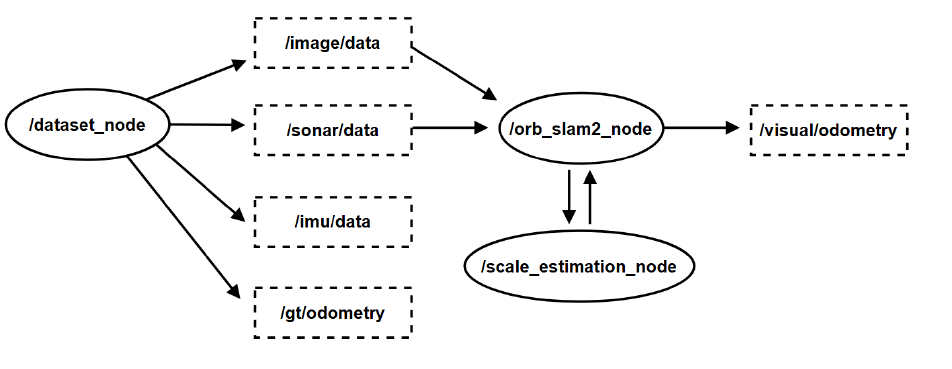 ROS2 topics, nodes, and service. (optional) Note: IMU data and groundtruth odometry are only used for EKF and evaluation
ROS2 topics, nodes, and service. (optional) Note: IMU data and groundtruth odometry are only used for EKF and evaluation
Capture data
Task: use HoloOcean simulation to generate synced camera images and sonar images
I assume you’ve already followed this doc and installed HoloOcean (I used version 1.0.0 with Unreal Enine 4.27)
In this blog, we’ll use a sample scenario ExampleLevel that I previously built for you, in which the HoveringAUV will move parallel to the surface of a large cube (similar to inspection).
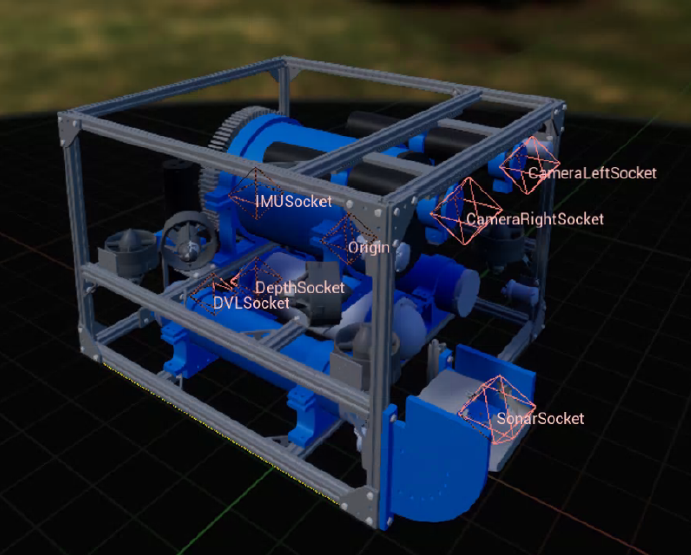
We first need to setup the configuration for AUV with its sensors. You can set the sampling rate at 30Hz so the output sensors data are synced.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
{
"name": "HoveringCamera",
"world": "ExampleLevel",
"main_agent": "auv0",
"ticks_per_sec": 180,
"frames_per_sec": true,
"octree_min": 0.02,
"octree_max": 30.0,
"scene_id": 1,
"agents":[
{
"agent_name": "auv0",
"agent_type": "HoveringAUV",
"sensors": [
{
"sensor_type": "DVLSensor",
"socket": "DVLSocket",
"Hz": 30,
"configuration": {
"Elevation": 22.5,
"VelSigma": 0.0,
"ReturnRange": false,
"MaxRange": 2,
"RangeSigma": 0.0,
"DebugLines": false
}
},
{
"sensor_type": "IMUSensor",
"socket": "COM",
"Hz": 30,
"configuration": {
"AccelSigma": 0.0,
"AngVelSigma": 0.0,
"AccelBiasSigma": 0.0,
"AngVelBiasSigma": 0.0,
"ReturnBias": false
}
},
{
"sensor_type": "RotationSensor",
"socket": "COM",
"Hz": 30
},
{
"sensor_type": "PoseSensor",
"sensor_name": "PoseSensorCOM",
"socket": "COM",
"Hz": 30,
"location": [0.07325, -0.02, -0.3179],
"rotation": [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
},
{
"sensor_type": "PoseSensor",
"sensor_name": "PoseSensorRGB",
"socket": "CameraRightSocket",
"Hz": 30,
"location": [0.1, -0.095, -0.205],
"rotation": [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
},
{
"sensor_type": "PoseSensor",
"sensor_name": "PoseSensorSonar",
"socket": "SonarSocket",
"Hz": 30,
"location": [0.0, 0.0, 0.205],
"rotation": [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
},
{
"sensor_type": "RGBCamera",
"sensor_name": "RightCamera",
"socket": "CameraRightSocket",
"Hz": 30,
"configuration": {
"CaptureWidth": 512,
"CaptureHeight": 512
},
"location": [0.1, -0.095, -0.205],
"rotation": [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
},
{
"sensor_type": "ImagingSonar",
"socket": "SonarSocket",
"Hz": 30,
"configuration": {
"RangeBins": 512,
"AzimuthBins": 512,
"RangeMin": 0.01,
"RangeMax": 3.5,
"InitOctreeRange": 10,
"Elevation": 10,
"Azimuth": 130,
"ShowWarning": false,
"ViewRegion": false,
"ViewOctree": -10
},
"location": [0.0, 0.0, 0.205],
"rotation": [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
}
],
"control_scheme": 0,
"location": [-5.597, 7.103, -6.15],
"rotation": [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
}
],
"window_width": 1024,
"window_height": 640
}
You can save this config as test-scene.json.
Next, we write a script to spawn a HoloOcean simulation, load the scene and AUV with this config file:
1
2
with holoocean.make('test-scene', show_viewport=True) as env:
### do further stuffs with AUV ...
, enter a loop ticking the environment states, then extract sensors data:
1
2
3
4
while True:
state = env.tick()
if 'RightCamera' in state and 'ImagingSonar' in state and 'PoseSensorRGB' in state and 'PoseSensorSonar' in state:
### extract rgb data, sonar data (in polar coordinate), and their ground-truth poses (can be used in evaluation)
, saving data:
1
2
cv2.imwrite(f"./out/rgb_{SCENE_ID}/{ts:.6f}.png", cam_img)
np.save(f"./out/sonar_{SCENE_ID}_polar/{ts:.6f}", polar_img)
Note: You should use a manually updated timestamp ts if you plan to use other sensors like IMU for EKF fusion purpose, since time.time() may depend on the running computer resource, and not reflect true simulation time.
The full script can be found in my repo
Once you run the script, the simulation window should open.
 HoloOcean simulation window - AUV observing cube scene
HoloOcean simulation window - AUV observing cube scene
Dataset node (Python)
Task: read data saved in directories, then publish messages
Initialize publishers, timers, file paths & names, ..
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
from sensor_msgs.msg import Imu, Image
from nav_msgs.msg import Odometry
class DatasetNode(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__("dataset_node_py")
self.publisher_rgb_ = self.create_publisher(Image, 'image/data', 10)
self.publisher_sonar_ = self.create_publisher(Image, 'sonar/data', 10)
self.publisher_imu_ = self.create_publisher(Imu, '/imu/data', 10) ## (optional) for EKF fusion
self.publisher_gt_ = self.create_publisher(Odometry, '/gt/odometry', 10) ## (optional) for comparison
self.timer_rgbsonar_ = self.create_timer((1/30)*10, self.timer_rgbsonar_callback)
self.timer_imu_ = self.create_timer((1/180)*10, self.timer_imu_callback) ## (optional) for EKF fusion
self.timer_gt_ = self.create_timer((1/30)*10, self.timer_gt_callback) ## (optional) for comparison
self.rgb_path = f"{self.get_parameter('base_path').value}/rgb_{self.get_parameter('num').value}/"
self.sonar_path = f"{self.get_parameter('base_path').value}/sonar_{self.get_parameter('num').value}/"
self.imu_path = f"{self.get_parameter('base_path').value}/imu_{self.get_parameter('num').value}/"
self.gt_path = f"{self.get_parameter('base_path').value}/poses_{self.get_parameter('num').value}/poses_rgb.txt"
self.rgb_fnames = sorted(glob.glob(f"{self.rgb_path}/*"), key=lambda x: int(x.split('/')[-1][:-4].replace('.','')))
self.sonar_fnames = sorted(glob.glob(f"{self.sonar_path}/*"), key=lambda x: int(x.split('/')[-1][:-4].replace('.','')))
self.imu_fnames = sorted(glob.glob(f"{self.imu_path}/*"), key=lambda x: int(x.split('/')[-1][:-4].replace('.','')))
For camera and sonar images, we use sensor_msgs.msg.Image. For ground truth odometry, we use nav_msgs.msg.Odometry.
Publishing camera and sonar images:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
def timer_rgbsonar_callback(self):
if self.idx_rgbsonar >= 0 and self.idx_rgbsonar < len(self.rgb_fnames):
if self.idx_rgbsonar==0: self.forward = True
ts = float(self.imu_fnames[self.idx_rgbsonar].split('/')[-1][:-4])
rgb_im = cv2.imread(self.rgb_fnames[self.idx_rgbsonar])
sonar_im = np.load(self.sonar_fnames[self.idx_rgbsonar])
timestamp = float(self.rgb_fnames[self.idx_rgbsonar].split("/")[-1][:-4])
msg_sonar = self.bridge.cv2_to_imgmsg((sonar_im*255).astype(np.uint8), encoding="mono8")
msg_sonar.header.stamp.sec = int(ts)
msg_sonar.header.stamp.nanosec = int((ts - int(ts)) * (10**9))
msg_sonar.header.frame_id = str(self.idx_rgbsonar)
msg_rgb = self.bridge.cv2_to_imgmsg(rgb_im.astype(np.uint8), encoding="bgr8")#sonar_im)
msg_rgb.header.stamp.sec = int(ts)
msg_rgb.header.stamp.nanosec = int((ts - int(ts)) * (10**9))
msg_rgb.header.frame_id = str(self.idx_rgbsonar)
self.publisher_sonar_.publish(msg_sonar)
self.publisher_rgb_.publish(msg_rgb)
if self.forward: self.idx_rgbsonar+=1
else: self.idx_rgbsonar-=1
if self.idx_rgbsonar == len(self.rgb_fnames):
self.done = f"{(int(self.done,base=2) | int('1000',base=2)):03b}"
Publishing ground truth odometry:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
def timer_gt_callback(self):
if self.idx_gt >= 0 and self.idx_gt < len(self.gt_poses):
ts, tx, ty, tz, qx, qy, qz, qw = [float(_) for _ in self.gt_poses[self.idx_gt].split()]
### align gt with odometry
if self.gt_pose_first is None:
self.gt_pose_first = [tx, ty, tz, qx, qy, qz, qw]
tx = -(tx - self.gt_pose_first[0])
ty = -(ty - self.gt_pose_first[1])
tz = tz - self.gt_pose_first[2]
######
### rotate orientation based on rotated origin 180
rot_mat = R.from_quat([qx, qy, qz, qw]).as_matrix()
rot_fix = np.array([
[-1, 0, 0],
[0, -1, 0],
[0, 0, 1]
])
rot_quat = R.from_matrix(rot_fix @ rot_mat).as_quat()
######
odom_msg = Odometry()
odom_msg.header.stamp.sec = int(ts)
odom_msg.header.stamp.nanosec = int((ts - int(ts)) * (10**9))
odom_msg.header.frame_id = "odom"
odom_msg.child_frame_id = "base_link"
odom_msg.pose.pose.position.x = tx
odom_msg.pose.pose.position.y = ty
odom_msg.pose.pose.position.z = tz
odom_msg.pose.pose.orientation.x = rot_quat[0]
odom_msg.pose.pose.orientation.y = rot_quat[1]
odom_msg.pose.pose.orientation.z = rot_quat[2]
odom_msg.pose.pose.orientation.w = rot_quat[3]
self.publisher_gt_.publish(odom_msg)
self.publisher_gt2_.publish(odom_msg)
self.idx_gt += 1
if self.idx_gt == len(self.gt_poses):
self.done = f"{(int(self.done,base=2) | int('0001',base=2)):03b}"
Monocular ORB-SLAM2 node (C++)
Task: subscribe to data topics, sync data + keypoints + 3D pointcloud, send packed data as request for scale correction
initialize subscriber, service client
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
MonocularSlamNode::MonocularSlamNode(ORB_SLAM2::System* pSLAM)
: Node("orbslam"),
m_SLAM(pSLAM)
{
client_cb_group_ = this->create_callback_group(rclcpp::CallbackGroupType::MutuallyExclusive);
timer_cb_group_ = this->create_callback_group(rclcpp::CallbackGroupType::MutuallyExclusive);
rclcpp::SubscriptionOptions options;
options.callback_group = timer_cb_group_;
m_image_subscriber = this->create_subscription<RgbSonar>(
"dataset_rgb_sonar",
10,
std::bind(&MonocularSlamNode::GrabImage, this, std::placeholders::_1),
options);
client_ = this->create_client<custom_interfaces::srv::FrameSlam>("scale_estimation", rmw_qos_profile_services_default, client_cb_group_);
/* initialize other stuffs .. */
}
GrabImage function handles callback to m_image_subscriber:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
void MonocularSlamNode::GrabImage(const RgbSonar::SharedPtr msg)
{
// Copy the ros image message to cv::Mat.
try
{
m_cvImPtr = cv_bridge::toCvCopy(msg->rgb_im);
}
catch (cv_bridge::Exception& e)
{
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "cv_bridge exception: %s", e.what());
return;
}
/* scale estimation & correction */
Tcw = m_SLAM->TrackMonocular(m_cvImPtr->image, msg->timestamp);
if (m_SLAM->mpTracker->newKeyFrameFlag){ // you need to modify ORB-SLAM2 source code to add newKeyFrameFlag checking if this current frame is a keyframe, then rebuild ORB-SLAM2
/* scale estimation (request) */
float scale = getScale(msg, Tcw);
if (scale != -1 && scale != 0 && scale > 0.01 ){ //&& scale < 1.20) { //&& scale < 1.10 ) { // !!!
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "[scale_estimation] scale = %f", scale);
if ( scaled==false || (scaled==true && (abs(scale-1.0) <= 0.05 ) ) ){ // for stable rescaling ..
cv::Mat cur_pose = m_SLAM->mpTracker->mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF->GetPose();
cur_pose.rowRange(0,3).col(3) = cur_pose.rowRange(0,3).col(3) * scale;
m_SLAM->mpTracker->mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF->SetPose(cur_pose);
/* rescale current frame's map points */
for (auto &mp : m_SLAM->mpTracker->mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF->mvpMapPoints){
if (mp != NULL){
mp->SetWorldPos(mp->GetWorldPos() * scale);
}
}
std::cout << "[!] scaled" << std::endl;
if (abs(1.0 - scale) <= 0.1 && rescaleCount >= 5)
scaled = true;
}
rescaleCount += 1;
}
else RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "[scale_estimation] failed.");
}
else {
m_SLAM->mpMapDrawer->curPointIndex.clear();
}
/****************/
/* publish odom message */
if (!Tcw.empty()){
cv::Mat Rwc = Tcw.rowRange(0,3).colRange(0,3).t();
cv::Mat twc = -Rwc * Tcw.rowRange(0,3).col(3); // !!!!
// convert to Right-hand coordinate system
cv::Mat R_fix = (cv::Mat_<float>(3,3) << 0, 0, 1,
-1, 0, 0,
0, -1, 0);
cv::Mat t_fix = (cv::Mat_<float>(3,1) << 0, 0, 0);
std::vector<float> q = ORB_SLAM2::Converter::toQuaternion(Rwc);
auto odom_msg = nav_msgs::msg::Odometry();
odom_msg.header.stamp.sec = floor(msg->timestamp);
odom_msg.header.stamp.nanosec = (msg->timestamp - floor(msg->timestamp)) * pow(10,9);
odom_msg.header.frame_id = "odom";
odom_msg.child_frame_id = "base_link";
odom_msg.pose.pose.position.x = twc.at<float>(2); //twc.at<float>(0);
odom_msg.pose.pose.position.y = -twc.at<float>(0); //twc.at<float>(1);
odom_msg.pose.pose.position.z = twc.at<float>(1); //twc.at<float>(2);
odom_msg.pose.pose.orientation.x = q[2]; //q[0];
odom_msg.pose.pose.orientation.y = -q[0]; //q[1];
odom_msg.pose.pose.orientation.z = -q[1]; //q[2];
odom_msg.pose.pose.orientation.w = q[3];
odom_msg.pose.covariance = {
3000.1, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 3000.1, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 1000000000000.001, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1000000000000.001, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1000000000000.001, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1000000000000.001
};
m_odom_publisher_->publish(odom_msg);
}
}
In the above code, it calls our getScale function for every keyframe.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
float MonocularSlamNode::getScale(const RgbSonar::SharedPtr msg, cv::Mat Tcw){
/* create request */
auto request = std::make_shared<custom_interfaces::srv::FrameSlam::Request>();
request->timestamp = msg->timestamp;
/* parse msg */
request->rgb_im = msg->rgb_im;
request->sonar_im = msg->sonar_im;
request->kps.clear();
request->mps.clear();
/* obtain current camera pose (to compute visual distance d) */
if (!Tcw.empty()){
cv::Mat Rwc = Tcw.rowRange(0,3).colRange(0,3).t();
cv::Mat twc = -Rwc * Tcw.rowRange(0,3).col(3); // !!!!
std::vector<float> q = ORB_SLAM2::Converter::toQuaternion(Rwc);
tf2::Transform tf2_transform;
tf2_transform.setOrigin(tf2::Vector3(twc.at<float>(0,0), twc.at<float>(0,1), twc.at<float>(0,2)));
tf2_transform.setRotation(tf2::Quaternion(q[0], q[1], q[2], q[3]));
geometry_msgs::msg::Pose pose_msg;
tf2::toMsg(tf2_transform, pose_msg);
request->rgb_pose = pose_msg;
}
/* obtain 2D keypoints and 3D map points (to compute visual distance d) */
for (int i=0; i<m_SLAM->mpTracker->mCurrentKeyPointsMapPoints.size(); i++){
cv::KeyPoint kpCur = m_SLAM->mpTracker->mCurrentKeyPointsMapPoints[i].first;
ORB_SLAM2::MapPoint *mpCur = m_SLAM->mpTracker->mCurrentKeyPointsMapPoints[i].second;
auto mpCurPos = mpCur->GetWorldPos();
KeyPoint kpVar;
kpVar.x = kpCur.pt.x;
kpVar.y = kpCur.pt.y;
MapPoint mpVar;
mpVar.x = mpCurPos.at<float>(0);
mpVar.y = mpCurPos.at<float>(1);
mpVar.z = mpCurPos.at<float>(2);
request->kps.push_back(kpVar);
request->mps.push_back(mpVar);
}
/* send request */
float scale = -1;
auto future = client_->async_send_request(request);
std::future_status status = future.wait_for(10s);
if (status == std::future_status::ready){
auto response = future.get();
if (response->timestamp == msg->timestamp){
scale = response->scale;
if (response->indexes.size() > 0 ){
m_SLAM->mpMapDrawer->curPointIndex.clear();
for (int i=0; i < response->indexes.size(); i++){
m_SLAM->mpMapDrawer->curPointIndex.push_back(response->indexes[i]);
}
}
else {
m_SLAM->mpMapDrawer->curPointIndex.clear();
}
}
else RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "[scale estimation] timestamp not matched.");
}
else if (status == std::future_status::timeout){
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "[scale_estimation] timeout.");
}
else if (status == std::future_status::deferred){
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "[scale_estimation] deferred.");
}
return scale;
}
Scale Estimation / Correction service node (Python)
Task: receive data request, estimate + correct scale, then respond the corrected scale
Initialize some configurations
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
### sonar config
azi = 120
phi = 10
minR = 0.01
maxR = 2
binsR = 512
binsA = 512
### camera config
W = 512
H = 512
fx = W/2 # fov = 90
fy = H/2
cx = W/2
cy = H/2
### camera-sonar config
baseline_y = 0.205
sonar_idx_arr = np.arange(-binsA/2, binsA/2+1, 1)
sonar_idx_arr = sonar_idx_arr[sonar_idx_arr != 0]
theta_i_arr = sonar_idx_arr * (azi/binsA)
u_i_arr = np.round(fx * np.tan((theta_i_arr/180) * np.pi) + cx).astype(int) # TODO: add +- theta_h
polar_mask = np.where((u_i_arr >= 0) & (u_i_arr <= W))[0]
## multi-beam in center (most accurate)
polar_mask = polar_mask[int(len(polar_mask)/2)-70 : int(len(polar_mask)/2)+70]
u_i_arr_masked = u_i_arr[polar_mask]
ranges = np.linspace(minR, maxR, binsR)
define some utility functions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
def extract_ranges(polar_img, idx_arr, maxR, binsR):
r_arr = np.ones(polar_img.shape[1]) * -1
intensity_min_idx_arr = np.ones(polar_img.shape[1]) * -1
for idx in idx_arr:
# breakpoint()
intensity_min_idx = np.argmax(polar_img[:, idx] > 0) #np.where(polar_img[:, idx] > 0)[0]
if intensity_min_idx > 0:
r_arr[idx] = ranges[intensity_min_idx]
intensity_min_idx_arr[idx] = intensity_min_idx
return r_arr, intensity_min_idx_arr.astype(int)
def compute_track_beam_idx(track_beam_idx_ref, azi, binsA, r_ref, relative_dist):
theta_ref = (track_beam_idx_ref - binsA/2)* azi / binsA
z_ref = r_ref * np.cos(theta_ref * np.pi/180)
x_ref = r_ref * np.sin(theta_ref * np.pi/180)
z_cur = z_ref + np.abs(relative_dist)
theta_cur = np.arctan(x_ref / z_cur) * 180 / np.pi
track_beam_idx_cur = int(theta_cur * binsA / azi + binsA/2)
return track_beam_idx_cur
Our main ScaleEstimationNode:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
class ScaleEstimationNode(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__("scale_est_node")
self.bridge_ = CvBridge()
self.rgb_trans_prev = None
self.declare_parameter('scene_id', rclpy.Parameter.Type.INTEGER)
self.scene_id = self.get_parameter('scene_id').value
self.server_ = self.create_service(srv.FrameSlam, "scale_estimation", self.callback_scale_estimation)
def callback_scale_estimation(self, request, response):
timestamp = request.timestamp
print(f"\n[scale_estimation] timestamp = {timestamp}")
rgb_im = self.bridge_.imgmsg_to_cv2(request.rgb_im)
sonar_im = self.bridge_.imgmsg_to_cv2(request.sonar_im)
kps = self.kpsmsg_to_kps(request.kps)
mps = self.mpsmsg_to_mps(request.mps)
rgb_trans = np.array([request.rgb_pose.position.x, request.rgb_pose.position.y, request.rgb_pose.position.z]) ### ORB_SLAM coord system
print(f"rgb_trans = {rgb_trans}")
rgb_im_kps = rgb_im.copy() #cv2.cvtColor(im, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
rgb_im_lines_min = rgb_im.copy()
sonar_im_flip = cv2.flip(sonar_im, 1)
r_arr, intensity_min_idx_arr = extract_ranges(sonar_im_flip, polar_mask, maxR, binsR)
### rgb_im_lines
v_range_arr = np.repeat(np.array([[-1,-1]]), len(u_i_arr_masked), axis=0 )
for i, idx in enumerate(polar_mask):
r = r_arr[idx]
if r != -1 and r != 0:
v_range_arr[i][0] = np.abs(fy/np.cos(theta_i_arr[idx]*np.pi/180)) * ((-r*np.sin(phi*np.pi/180) - baseline_y)/ (r*np.cos(phi*np.pi/180)) ) + cy #+ 25 #30 # 65 #85
v_range_arr[i][1] = np.abs(fy/np.cos(theta_i_arr[idx]*np.pi/180)) * ((-r*np.sin(-phi*np.pi/180) - baseline_y)/ (r*np.cos(-phi*np.pi/180)) ) + cy #+ 25 #30 # 65 #85
### rgb_im_lines_min
for i, u_i in enumerate(u_i_arr_masked):
v_range = v_range_arr[i]
cv2.line(rgb_im_lines_min, (u_i, v_range[0]), (u_i, v_range[1]), color=(0,255,0), thickness=1)
# print(f"heyy {v_range}")
### sonar_im_flip
sonar_im_flip = cv2.cvtColor(sonar_im_flip, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
for r_idx in polar_mask:
if r_arr[r_idx] != -1:
cv2.circle(sonar_im_flip, (r_idx, intensity_min_idx_arr[r_idx]), radius=2, color=(0,255,0), thickness=1)
### select closest 3D points (to sonar) in each beam
mp_min_arr = []
kp_min_arr = []
kp_min_idx_arr = []
for i, u_i in enumerate(u_i_arr_masked):
d_min = 999999
mp_min = None
kp_min = None
kp_min_idx = None
for j, kp in enumerate(kps):
if kp[0] == u_i:
v_range = v_range_arr[i]
if kp[1] >= v_range[0] and kp[1] <= v_range[1]:
if d_min >= np.abs(rgb_trans[2] - mps[j][2]):
d_min = np.abs(rgb_trans[2] - mps[j][2])
mp_min = mps[j]
kp_min = kp
kp_min_idx = j
mp_min_arr.append(mp_min)
kp_min_arr.append(kp_min)
kp_min_idx_arr.append(kp_min_idx)
scales = []
d_est_arr = []
err_arr = []
r_arr_ = []
for i, mp_min in enumerate(mp_min_arr): #mp_min_arr): # same len as u_i_arr_masked
r_i = r_arr[polar_mask][i]
if mp_min is not None and r_i != -1:
err_i = np.abs(r_i - np.sqrt(r_i**2 + baseline_y**2))
err_arr.append(err_i)
r_arr_.append(r_i)
### [elevation=10, PoI] d_true = dist(rgb_trans, mps[i])
d_est_i = np.linalg.norm(rgb_trans - mp_min)
## baseline
scale_i = r_i / d_est_i
d_est_arr.append(d_est_i)
scales.append(scale_i)
cv2.circle(rgb_im_kps, kp_min_arr[i], color=(0,255,0), radius=3, thickness=2)
scale = np.mean(scales) if len(scales)>0 else -1.0
print(f"scale = {scale} - len(kp_min_arr != None) = {len([_ for _ in kp_min_arr if _ is not None])}")
print(f"kp_min_idx_arr = {[_ for _ in kp_min_idx_arr if _ is not None]}\n")
if self.rgb_trans_prev is None:
self.rgb_trans_prev = rgb_trans
out_im = np.hstack((rgb_im_kps.astype(float)/255., rgb_im_lines_min.astype(float)/255., sonar_im_flip))
cv2.imshow("", out_im)
cv2.waitKey(1)
self.rgb_trans_prev = rgb_trans
### response
response.timestamp = timestamp
response.scale = scale
response.indexes = [_ for _ in kp_min_idx_arr if _ is not None]
return response
def kpsmsg_to_kps(self, kpsmsg):
kps = []
for kp_msg in kpsmsg:
kps.append(np.round((kp_msg.x, kp_msg.y)).astype(int))
# kps.append((kp_msg.x, kp_msg.y))
return kps
def mpsmsg_to_mps(self, mpsmsg):
mps = []
for mp_msg in mpsmsg:
mps.append([mp_msg.x, mp_msg.y, mp_msg.z])
return mps
The full script can be found in my repo
Results
Once you colcon build the package, you can run the scripts with these commands in three separate terminals:
1
2
# terminal 1: monocular ORB-SLAM2 node
ros2 run ros2_orbslam mono /home/bachnguyen/Desktop/SLAM/slam/ORB_SLAM2/Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt /home/bachnguyen/Desktop/SLAM/active-slam/pyslam/settings/HOLO.yaml
1
2
# terminal 2: scale_recover node
ros2 run scale_recover scale_est_node --ros-args -p scene_id:=[YOUR_SCENE_ID]
1
2
# terminal 3: dataset node
ros2 run dataset_reader dataset_node --ros-args -p base_path:=/home/bachnguyen/Desktop/SLAM/slam/holoocean/HoloOcean/tests/out/ -p num:=[YOUR_SCENE_ID]
You should start dataset_node last.
Here are some final results:
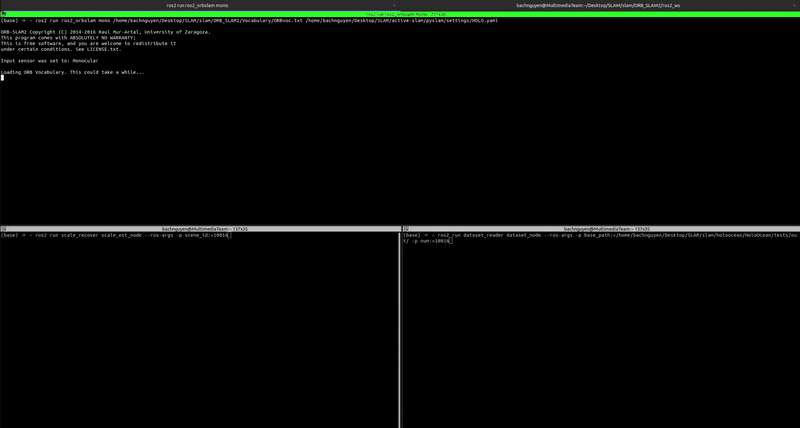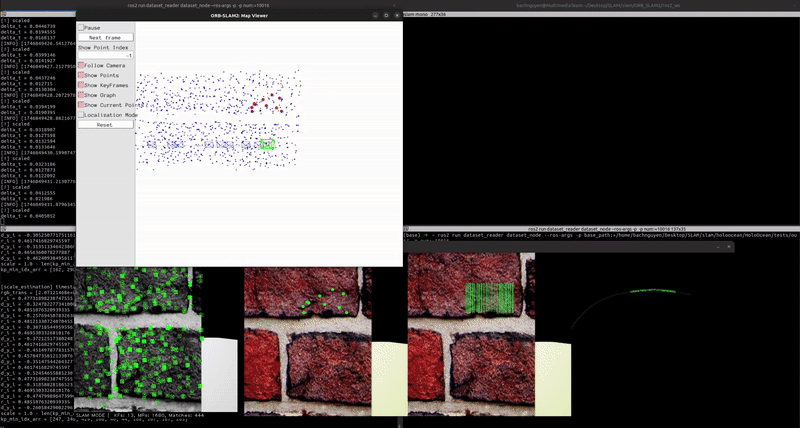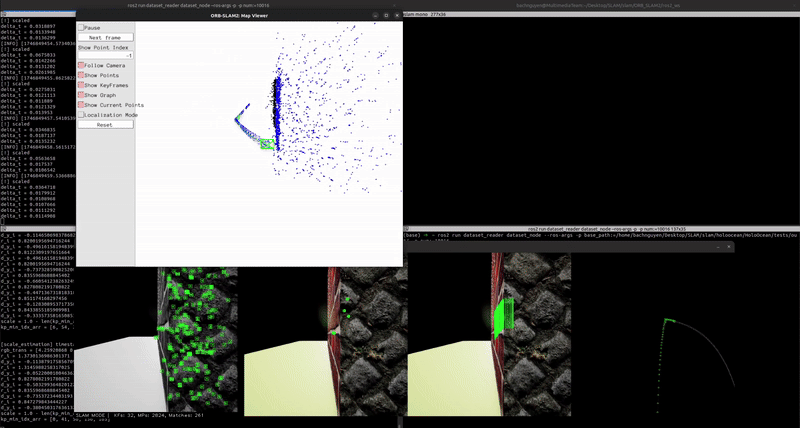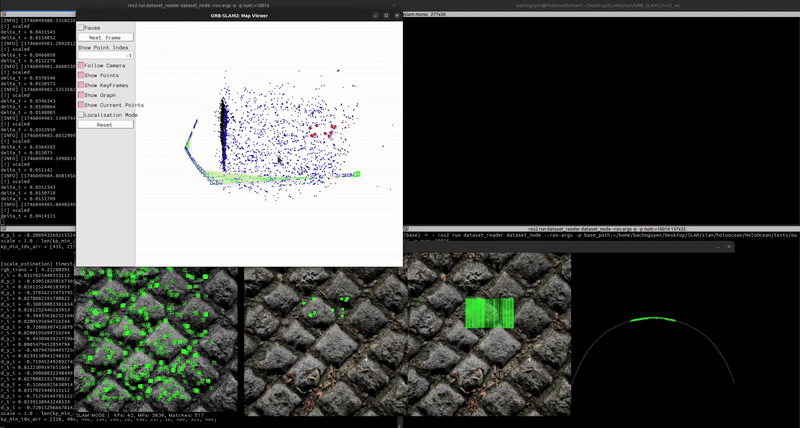 Localization & Mapping (without scale correction)
Localization & Mapping (without scale correction)
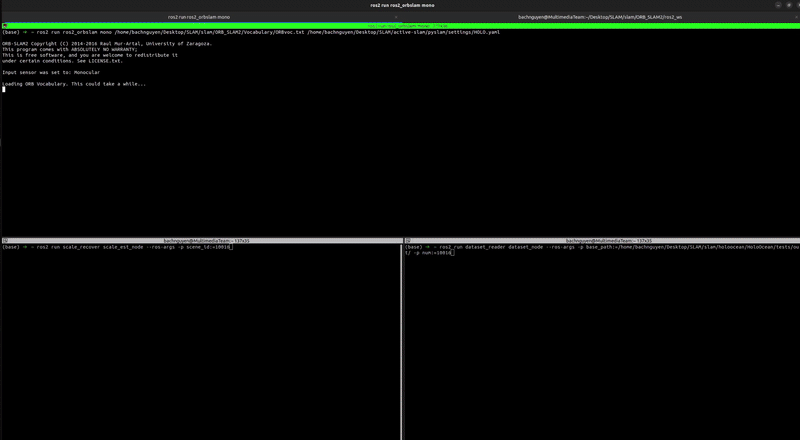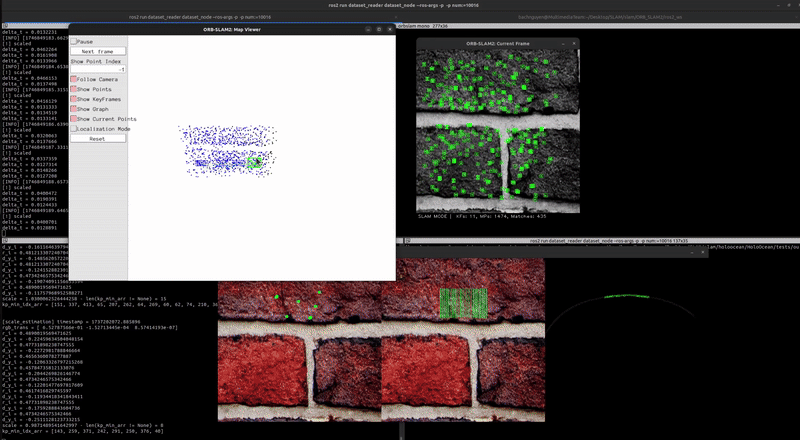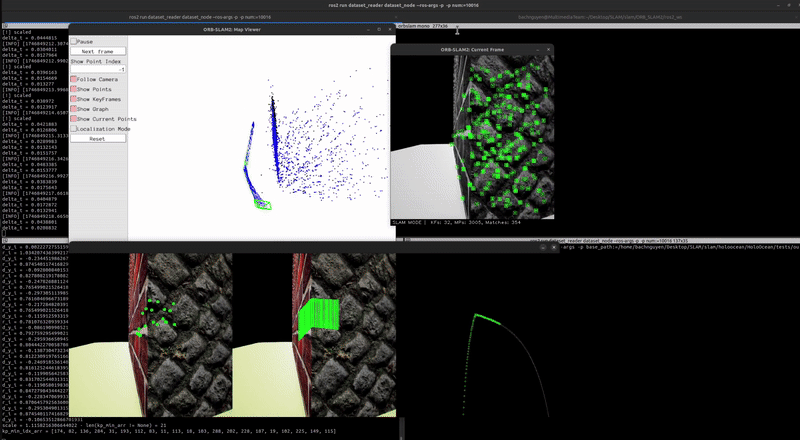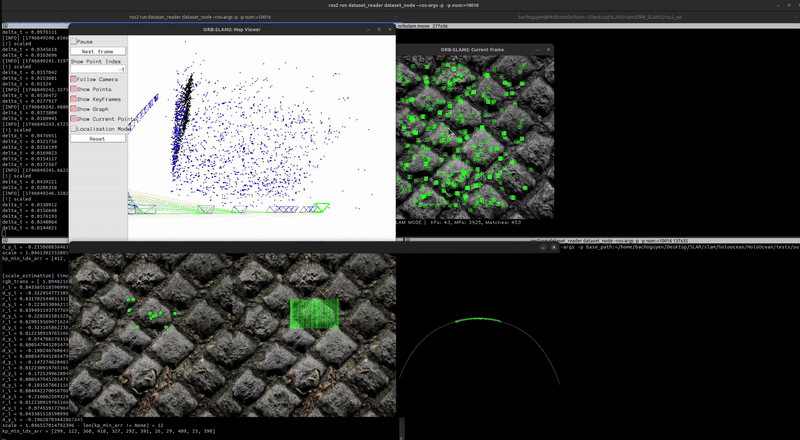 Localization & Mapping (with scale correction)
Localization & Mapping (with scale correction)
You can see the mapping has been rescaled using the scale_recover node.
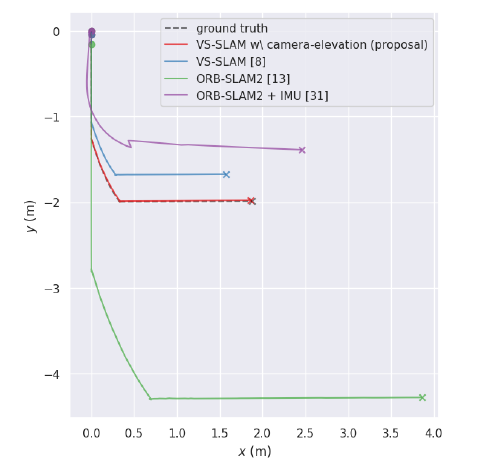
Additionally, this is further evaluation of Localization between different methods.
The above re-scaling code results in the final trajectory denoted VS_SLAM [8]. The approximation \(d_{true} / d_{est}\) ~ \(r / d_{est}\) is not accurate for close distances like in Close Visual Inspection (CVI) missions. In the next post, I will show you an improved rescaling ratio (VS_SLAM (proposal) in above figure) that can be applied for both close and far stand off distances between AUV and target object.
Thank you for reading ^^